APOPTOSIS IN MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION:
“IN VIVO“ VIZUALIZATION IN HUMANS
Skromne Kadlubik G. & Hidalgo Rico R. M. D.
From: The Radionucleidic Laboratory. Depto of Physiology.
Fac. Medicine. U.N.A.M. Mexico City, Mexico
In 1972 Kerr Wyllie and Currie described for the first time the term of “Apoptosis“(1). They called “Apoptosis“ the programed nature of the observed cell death. The term is derived from Greek: an described the described the “dropping- off “ or “falling off “ of leaves from trees, or petals from flowers. And is practically the “suicides“ of the cells in an altruistic form vs. the necrotic cells that are dying from gross physical or chemical insults.
Apoptosis have been described in neurodegenerative disordes like Alzheimer disease(2); in anemic syndromes with low eritropeyetin(3), in ulcer peptic disease from helicobacter pylori(4), and in other patologies. Also in experimental myocardial infarction the apoptosis fenomena have bee recently described(5). We use the Caspasa inhibidor: Acey1-DEVD-aldehido labaell with Tecnisium –99-me-taestable for the “in vivo“ visualization of the apoptosis in humans with myocardial infarction: and the present report is the experience we make in this field.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
We labell the following compound whit Tecnesium-99-metastabale: Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-CHO-Tc-99m.
The compound is: Acetyl-DEVD-Aldehyd and is an inhibitor of the interleucin convertidor enzyme (ICE inhibitor)(6). The method of labelling is whit Cloramin-T (7). Whit this new radiopharmaco we take myocardial scan in-six healthy volunteers to know the normal image of apoptosis in heart and compared with six myocardial infarction (acute) in an homologous poblation. Both patients and healthy volunteers, were observed during six months of follow-up to determined the possible reactions that the new radiopharmaco could do.
RESULTS:
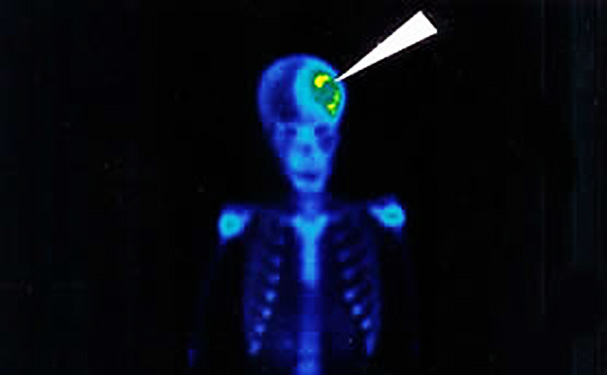
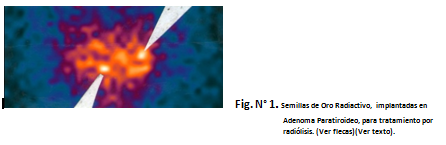
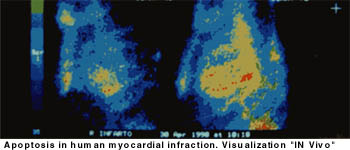
Fig. No. 1 represents the common image of the apoptosis in myocardial infarction take inmediatly post endovenous inyection with ICE inhibitor radiolobell whit Tecnesium 99 metaestabel (Tc-99 m): with a SPECT camera. Contrarly to this image, the normal myocard, don´t present apoptosis captation (“negative image”) vs. the “positive image” of apoptosis captation in myocardial infarction.
Nobody of the patient or normal volunteers present adverse reaction or complications for the application of this new radiopharmaco and method in six months of “follow-up”.

DISCUTION:
Altough apoptosis ocure in normal condition in some tissues: it seems entirely feasible that inapropiate apoptosis feature in many diseases, in combination with a necrotic form of cell death. This may ocurr in myocardial infarction and have obviously exciting clinical implications. In the present work we demostrated that there is apoptosis in human myocardial infarction: and can seen “in vivo“ with scan using an anticaspasa inhibitor labell whit radionuclides gamma emisors. This open a great research oportunity to investigate the of apoptosis insuch patology and if it is possible to mangement for the health of the patients; but deserves more studies.
CONCLUSIONS:
1. We labell the compound: “Acety- DEVD- Aldehyd“ with Tecnesium 99 metaestabel. Radiactive (anticaspasa inhibitor).
2. Whit this new radiopharmaco we take myocardial scan in six healthy volunteers.
3. We also take this studies in six patient with acute myocardial infarction.
4. The normal volunteers present a negative image of apoptosis of the hearth: there was no captation of the raidiopharmaco.
5. The patient with myocardial infarction presents a “positive image“ of apoptosis with captation of the radiopharmaco.
6. Both patients and volunteers were observed during six month of “follow-up” and don’t present adverse reactions or complications whit the new method and radiopharmaco.
7. The obviously clinical implication of this findings; and the simplicity of the method open a new great research opportunity in clinical cardiology; that requiered much more work for the clear dilucidation of apoptosis implication in myocardial infarction.
ABSTRACT:
We labell an anticaspasa inhibitor compound with radionuclides (Tecnesium 99 metestabel) and take scan image in six normal volunteers and six patients with acute myocardial infarction. The normal volunteers don’t have captation of the radiactive anticaspasa (“Negative image“) vs. the “positive image“ that occure in the myocardial infarction in all the patients studied. No body of the patients or volunteers have reactions or complication during six months of “follow- up“ after the use of the new radiopharmaco and method. The roll and clinical implication of apoptosis in myocardial infarction and the facilities of his “in vivo” visualization without damage, deserves more research in this exciting new camp of cardiology.
BIBLIOGRAPHY:
1.- Kerr. J.F.R.; Wyllie. A.H.: Currie. A. R. Apoptosis. Br. J. Cancer 26. 239-257 ( 1972): 2.- Choi, D.W. Current Opinons in Neurobiology 6. 667-672 ( 1996 3.- Genong F. W. Review of medical physiology. Capter VI. Circulation Appleton & Lange ( 1997 ). 18 th. Ed. (1997).
4.- Genta Robert M. Helicobacter fylori. Informmation, mucosal damage and apoptosis. Gasstroenterology 113 : 552-s-55. (1997).
5.- Akiyama R. et. Al Apoptosis in experimental myocardial infarction. Tissue Cell. Dec. 29 (6). 733-43. (1997).
6.- Tewari M. Quan. L. T. O´Rouke K. Et. Al. Call 81. 801-809 (1995).
7.- Early Pal J. & Bruce Sodee Principles and practice of Nuclear Medicine. 2do. Ed. Capter 8; Radiopharmaceuticals. Mosby ed. (95).